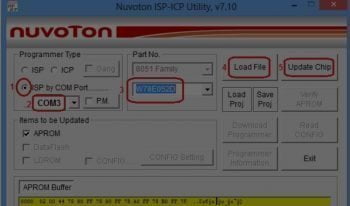
This Project is Suitable for Everyone Including student and Professional

Bluetooth-based relay control using an 8051-based microcontroller involves using Bluetooth communication to remotely control the switching of a relay. Here’s a general overview of the system:
- Hardware components:
- 8051-based microcontroller board
- HC-05 Bluetooth module
- Relay board
- Power supply
- AC Bulb 230v
- Bulb Holder
- Android based Mobile phone
- Connections:
- The HC-05 module is connected to the microcontroller’s serial port pins.
- The relay board is connected to the microcontroller’s output pins.
- Power supply connections are made to power the microcontroller and the relay board.
- Software:
The software for this system involves two main parts:
- Code for the microcontroller to receive commands from the Bluetooth module and switch the relay on or off accordingly.
- An Android application to send Bluetooth commands to the HC-05 module.
- Operation:
- The Android application sends Bluetooth commands to the HC-05 module.
- The HC-05 module receives the commands and sends them to the microcontroller.
- The microcontroller interprets the commands and switches the relay on or off based on the command received.
Overall, this system provides a wireless means of controlling a relay, which can be useful for a variety of applications, such as home automation or industrial control systems.
#include<reg51.h>
sbit X = P1^0; // connect relay1 to P1.0
sbit Y = P1^1; // connect relay2 to P1.1
void delay(unsigned int count)
{
unsigned int i;
while(count)
{
i = 115;
while(i > 0)
i--;
count--;
}
}
/*
Uart initialization function, call this function by passing a valid baud rate value to initialize UART
currently Supported Baud Rates are 9600,4800,2400,1200
*/
void uart_init(unsigned int baud)
{
unsigned int a = 9600, b = 4800, c = 2400 , d = 1200;
TMOD = 0x20; // timer 1 8-bit auto-reload
SCON = 0x50; // Tx and Rx enable
if(baud == a)
{
TL1 = 0xFD;
TH1 = 0xFD;
}
if(baud == b)
{
TL1 = 0xFA;
TH1 = 0xFA;
}
if(baud == c)
{
TL1 = 0xF4;
TH1 = 0xF4;
}
if(baud == d)
{
TL1 = 0xE8;
TH1 = 0xE8;
}
TR1 = 1; // Start timer
}
/*~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Trasmitting 8 bit data
Send 8-bit data while callinjg this function
to send it over UART
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~*/
void uart_write(unsigned char value)
{
SBUF = value;
while(!TI);
TI = 0;
}
/*~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Receiving 8-bit data
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~*/
char uart_read()
{
while(!RI);
RI = 0;
return(SBUF);
}
/*~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Xmitting String
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~*/
void uart_write_text(char *str)
{
unsigned char i=0;
while(str[i])
uart_write(str[i++]);
}
/*~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Read a particular number of bytes in a string
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~*/
void uart_read_text(void *buff, unsigned int len)
{
unsigned int i;
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
((char*)buff)[i]=uart_read();
}
}
/*~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Echoing received data
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~*/
void uart_echo()
{
uart_write(uart_read());
}
void main()
{
unsigned char byte;
uart_init(9600);
//P2 = 0x00;
X=0;
Y=0;
delay(100);
uart_write_text("Welcome");
while(1)
{
byte = uart_read(); // receive a byte serially, wait 1 second and again send it back
if(byte == 'A')
{
X = 1;
}
if(byte == 'a')
{
X = 0;
}
if(byte == 'B')
{
Y = 1;
}
if(byte == 'b')
{
Y = 0;
}
delay(100); // little delay so that user can recognize it
uart_write(byte); // resend received data over UART
}
}
for more learning of Python Raspbery Pi, Internet of things , ESP 32 ,and Arduino click on courses